In the quest for Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) compliance, senior executives are mobilizing to transform their organizations. While CEOs set the vision, CFOs ensure regulatory adherence, and CSOs craft sustainability strategies, CIOs have often been relegated to a supporting role. This must change.
5 CIO ‘Superhero Powers’ for a sustainable future
CIOs are the linchpins of sustainable transformation, and it’s time to unleash their potential. With their unique combination of technological expertise, strategic foresight, and problem-solving ability, CIOs are the superheroes within organizations that are able to tackle ESG challenges head-on.
Here are five ‘Superhero Powers’ every CIO can embrace to steer their organizations into a sustainable future.
Superhero Power 1: Lead the CSRD Journey
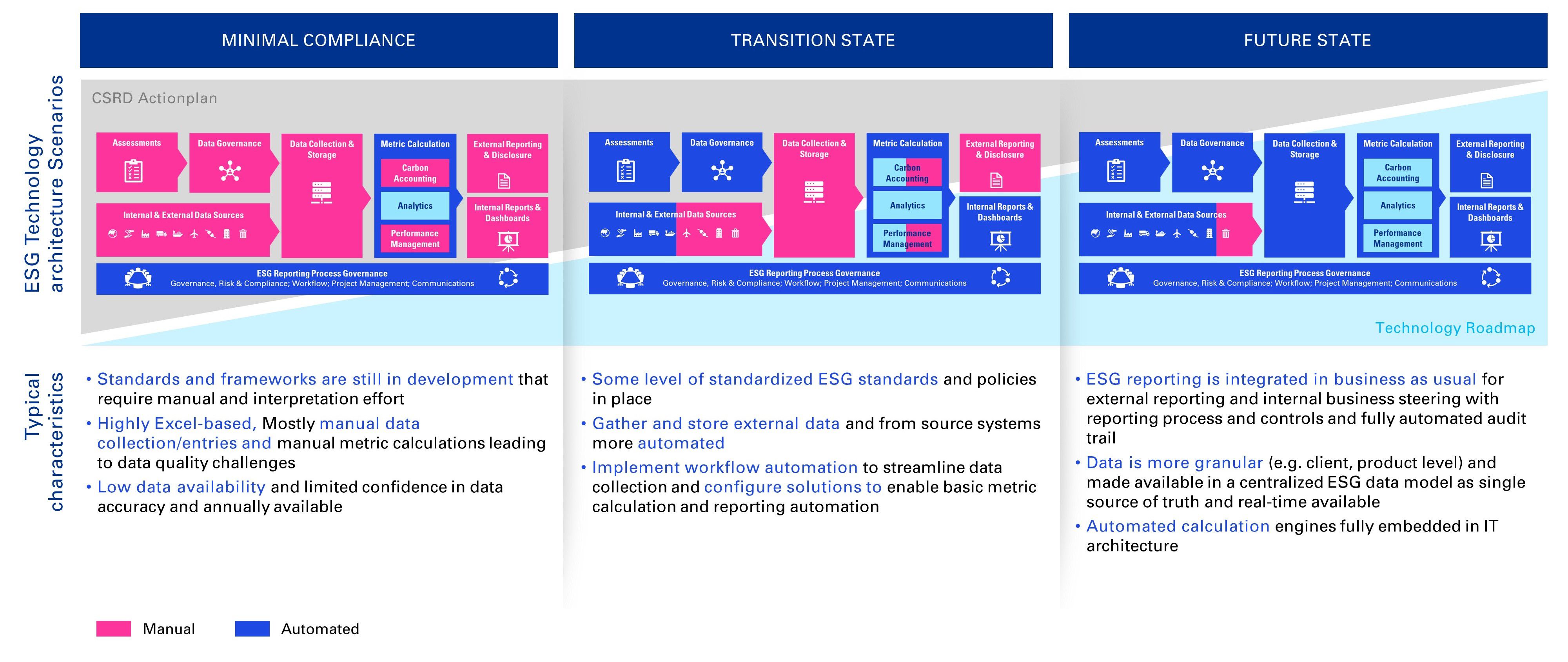
Every journey needs a guide, and the CSRD journey is no different. CIOs must take the reins to ensure organizations progress through the three stages of compliance:
- Minimal Compliance: ensure foundational systems are in place to meet immediate regulatory needs.
- Transition State: integrate and automate workflows, leveraging data for meaningful performance management.
- Future State: Envision and deliver cutting-edge ESG IT architectures that provide centralized, real-time data and fully automated (reporting) processes.
Unlocking the superhero power:
Take charge of your organization’s CSRD roadmap. Inspire your team by laying out a vision of not just compliance but leadership in sustainable innovation.
Superhero Power 2: Elevate ESG Maturity Levels
CIOs hold the keys to unlocking organizational maturity in ESG reporting. At every level, their influence can catalyze transformation:
- Minimal compliance: build reliable manual systems with strong data controls
- Transition state: introduce scalable technology solutions to enhance integration and automation
- Future state: drive the adoption of centralized ESG platforms, turning data into a competitive advantage
Unlocking the superhero power:
Challenge yourself to think beyond compliance. Position your organization at the forefront of ESG maturity by setting a clear path toward automated, insightful reporting systems (including smart controls).
Superhero Power 3: Transform Data into Strategic Insights for ESG performance steering
CIOs are the architects of actionable insights. It’s not enough to collect ESG data - context is king. With advanced analytics and dashboards, CIOs can translate raw numbers into a compelling narrative that fuels decision-making.
Unlocking the superhero power:
Work closely with your leadership team to understand key ESG metrics that drive the business (based on the Double Material Assessment). Deploy analytic tools that turn data into clarity and empower decision-makers with real time insights in a controlled way.
Superhero Power 4: Navigate the ESG Tech Maze
The ESG landscape is complex, and there is no silver bullet. But with their technical expertise, CIOs can shed a light on the right path through the maze of solutions.
Unlocking the superhero power:
Coordinate the necessary actions to facilitate a secure and effective CSRD (reporting) platform:
1. End-to-end Platforms: ensure workflows are optimized from data entry to reporting dashboards.
2. Data Governance: implement secure, scalable systems for managing & controlling internal and external ESG data.
3. Specialized tools: leverage niche products for high-priority metrics like carbon accounting.
4. System integration: seamlessly connect ESG processes with core business systems for maximum efficiency.
Superhero Power 5: Green IT - Your Gateway to Sustainable Operations
CIOs are uniquely positioned to drive Green IT initiatives, creating IT ecosystems that are as sustainable as they are efficient. By adopting energy-efficient data centers, sustainable software solutions, and responsible procurement policies, CIOs reduce the environmental footprint of technology operations.
Unlocking the superhero power:
Audit your IT landscape for its carbon footprint. Replace outdated systems with energy-optimized solutions, and become the champion of sustainable innovation at your organization.
Role of the CIO
CIOs are not strangers to tackling complexity. Whether it’s overcoming data quality issues, automating manual workflows, or aligning IT strategies with business goals, CIOs thrive on challenges. These hurdles are your opportunity to shine, to lead your organization with confidence and vision.
So, unleash your superhero powers. Lead the Green IT revolution, master the CSRD journey, and inspire your organization to redefine its ESG ambitions. Your unique skills can turn ESG from a compliance exercise into a strategic advantage, positioning your organization as a leader in sustainability.
For more insights on how technology can support ESG transformation, refer to CSRD: mastering data & technology - Compact or contact our experts Maurice op het Veld and Iris Hurenkamp.
Glossary: key CSRD abbreviations and definitions (also for the CIO)
Carbon Footprint |
Total CO₂ emissions from an organization’s operations |
CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive) |
EU directive mandating comprehensive sustainability and non-financial reporting for listed companies per 2024 and other companies as of 2025. |
DEI (Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion) |
Practices ensuring diversity, fairness, and inclusion within the workforce |
Double Materiality |
Determining material reporting topics both how ESG factors impact the organization and how the organization impacts society and the environment |
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) |
Framework for sustainable business practices and reporting |
ESRS (European Sustainability Reporting Standards) |
Standards developed by EFRAG (European Financial Reporting Advisory Group) for CSRD reporting |
EU Taxonomy |
EU classification system defining what qualifies as a sustainable activity |
GHG (Greenhouse Gas) |
Gases contributing to global warming, often reported as emissions scopes |
Scope 1, 2, 3 |
Scope 1: Direct emissions from owned or controlled sources Scope 2: Indirect emissions from purchased electricity, heating, or cooling Scope 3: Emissions from the value chain, including suppliers and customers |




